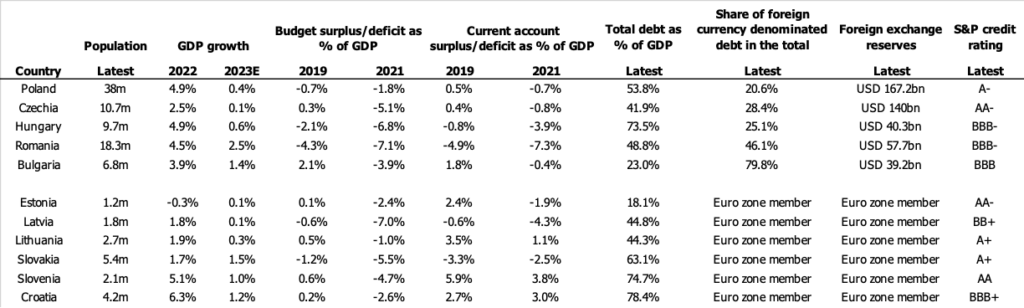
In this blog post, we analyze the public finances of the EU member states that before 1990 were part of the Soviet bloc. Slovenia, Slovakia, Croatia, Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania are already members of the Euro zone and thus do not have control over their currency. When it comes to the budget and current account deficits, we have compared the most recent data from 2021, which was affected by the pandemic, with the pre-COVID year 2019. While our analysis concludes that Poland, Czechia, Estonia and Slovenia are relatively reliable debtors, the condition of public finances in Hungary, Romania and Bulgaria looks much riskier.
Sources: Eurostat, central banks, tradingeconomics.com, Worldbank, S&P, CIA World Factbook
Especially after the PiS (Law and Justice party)-led government came to power in 2015, the Polish economy has been supported a lot through various social programs e.g. the “500+” child benefit, “Dobry Start” PLN 300 one-off support for pupils and the one-off retirement payment of PLN 1,100 “Emerytura+”. While these programs are considered negative by many economists as they stimulate consumption instead of investments, apparently they have not increased the debt level as well as budget and current account deficits in Poland as much as similar measures in Hungary. Especially a high current account deficit, which reflects imports and exports of goods and services, payments to foreign holders of a country’s investments, payments received from investments abroad, and transfers such as foreign aid and remittances, can negatively affect the foreign exchange rate of a country’s currency. On the one hand, a weak currency makes exports more profitable, however on the other makes the import of important components, the servicing of foreign debt or popular consumption goods more expensive.
Apart from Poland, Czechia is another non-Euro country, whose public finances look solid. What is particularly impressive, are its significant foreign exchange reserves, which are 3.5 times higher than in Hungary that however has a similar population. The larger the foreign exchange reserves, the better a country can fight pressure on its own currency.
In Romania and Bulgaria, especially the relatively high share of foreign currency denominated debt is worrying, which can lead to issues with repayment of debt in case the local currency significantly weakens versus EUR or USD.
Based on the methodology of S&P, Hungary’s and Romania’s current BBB- rating is the weakest investment grade rating. The rating agency’s definition is as follows: “An obligation rated ‘BBB’ exhibits adequate protection parameters, however adverse economic conditions or changing circumstances are more likely to lead to a weakened capacity of the obligor to meet its financial commitment on the obligation.” Estonia, whose debt only equals 18.1% of its GDP, and Czechia both have an AA- rating. According to S&P, it “differs from the highest-rated obligations only to a small degree”. Of all ex-communist EU member states, Slovenia has the best S&P credit rating (AA).